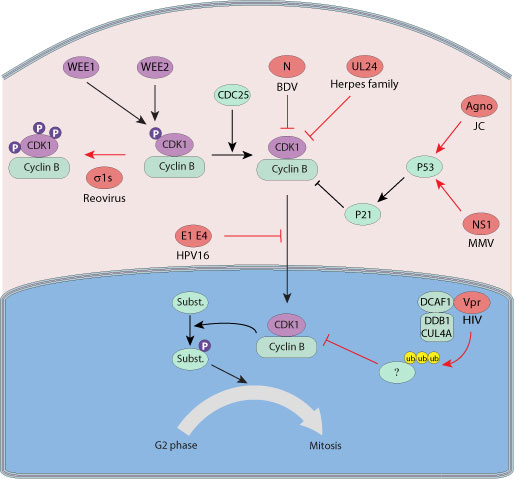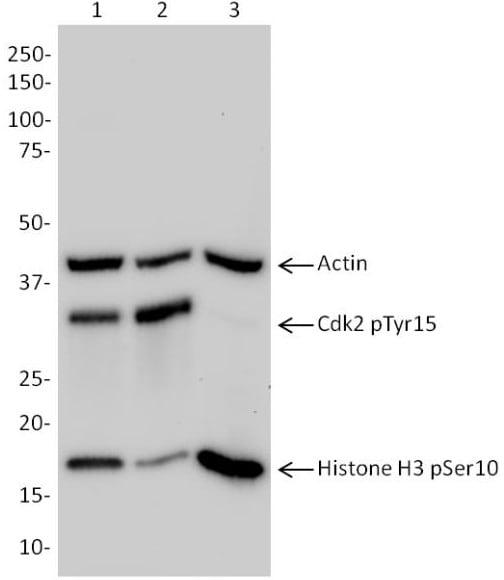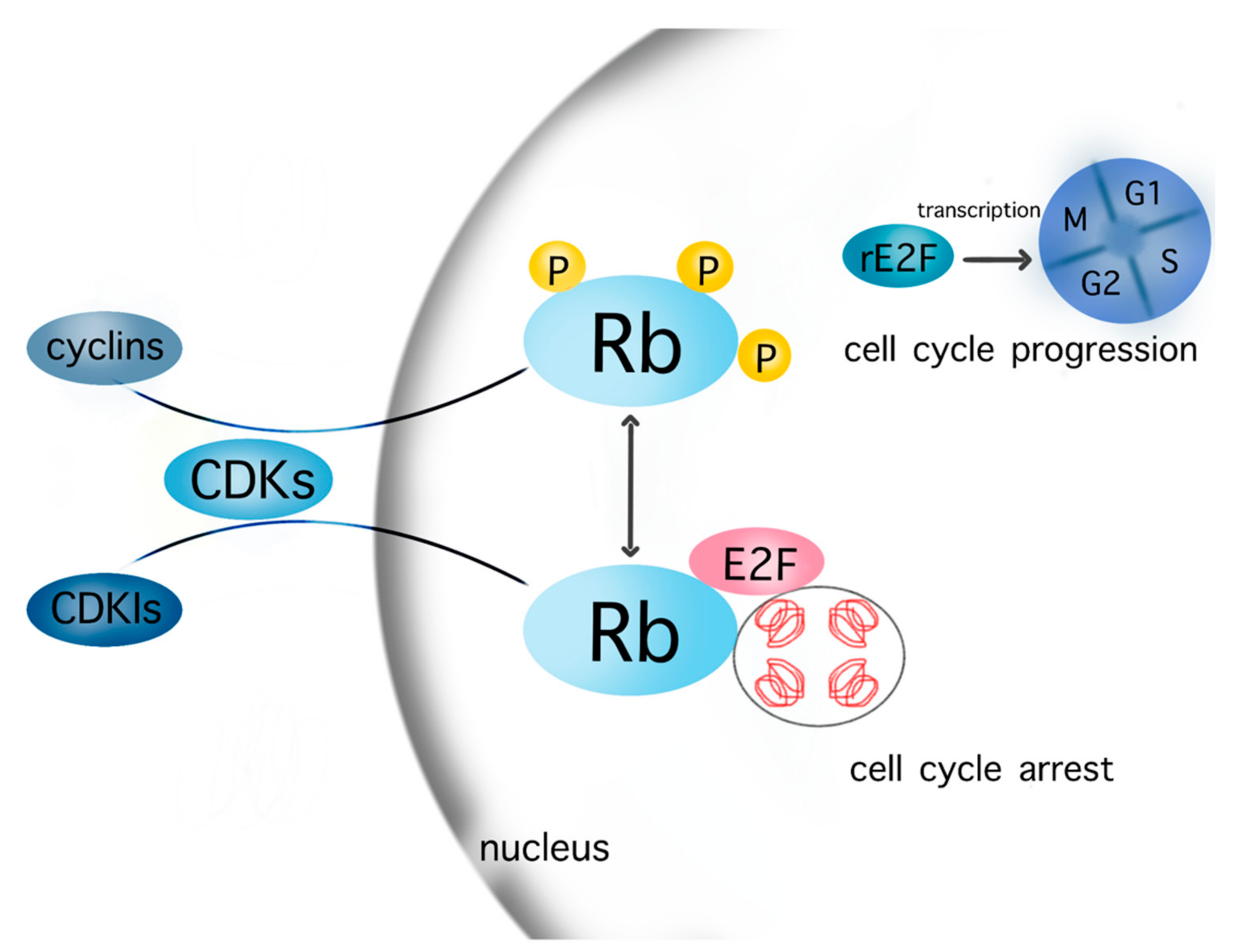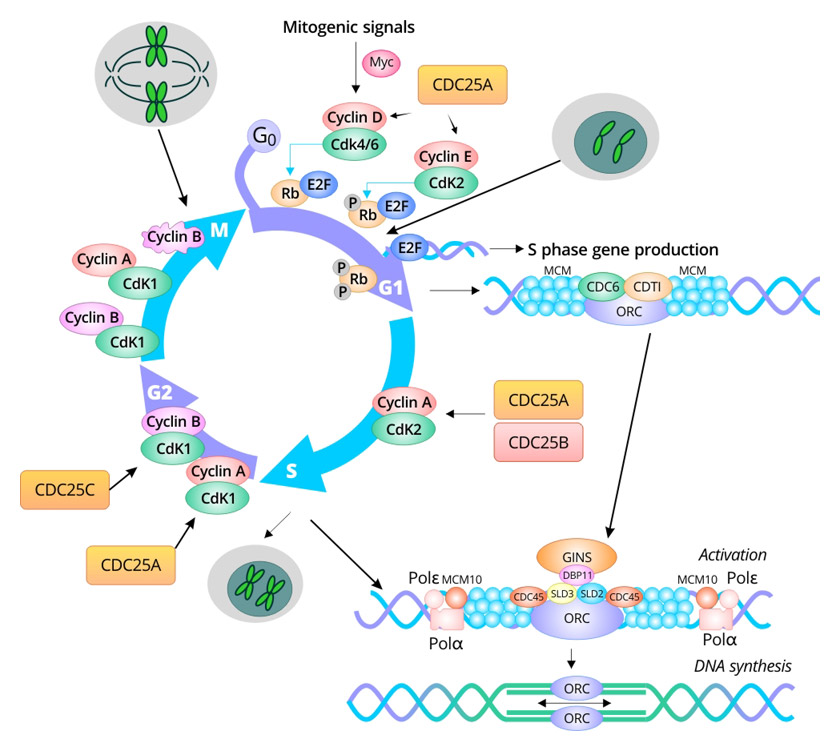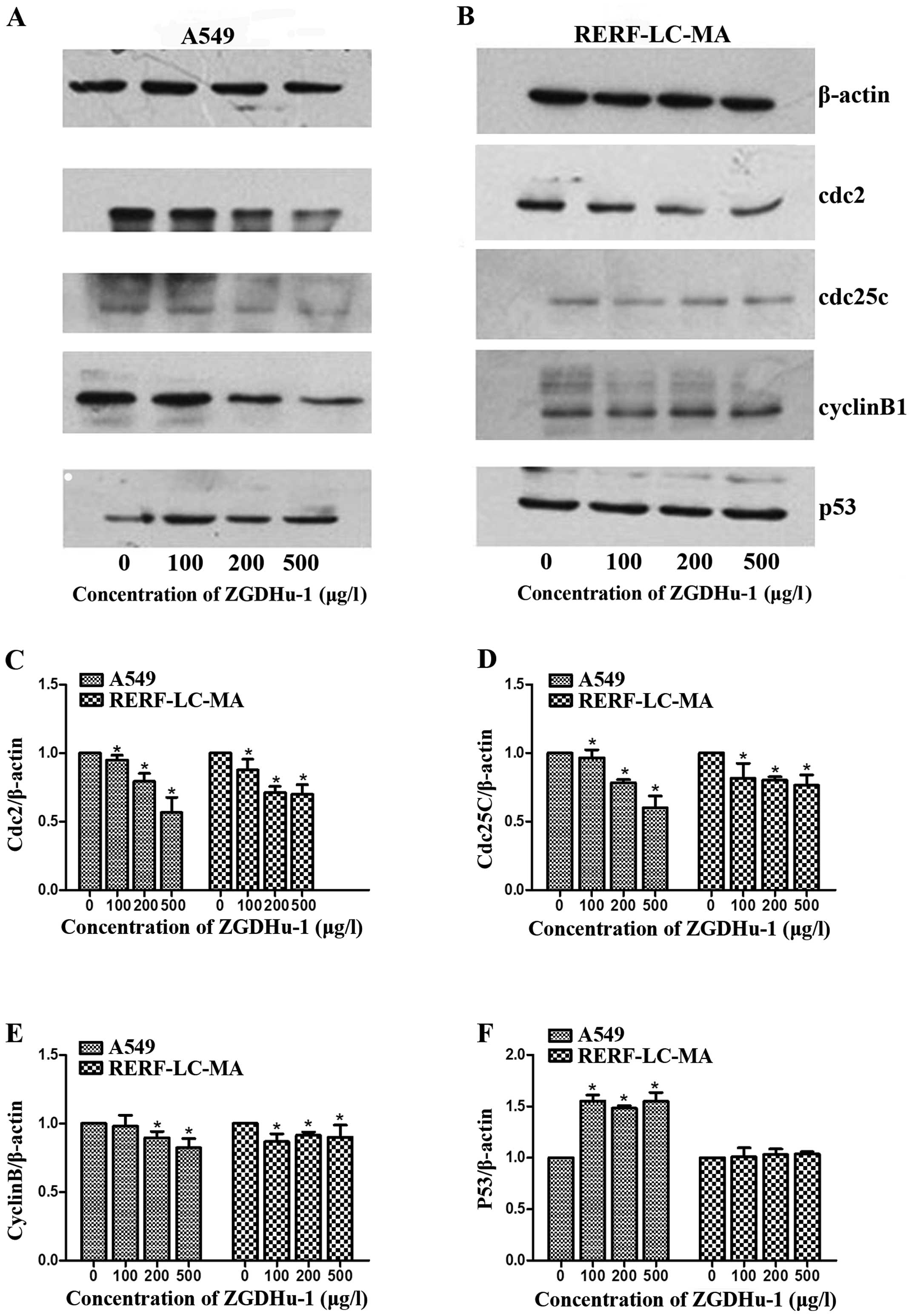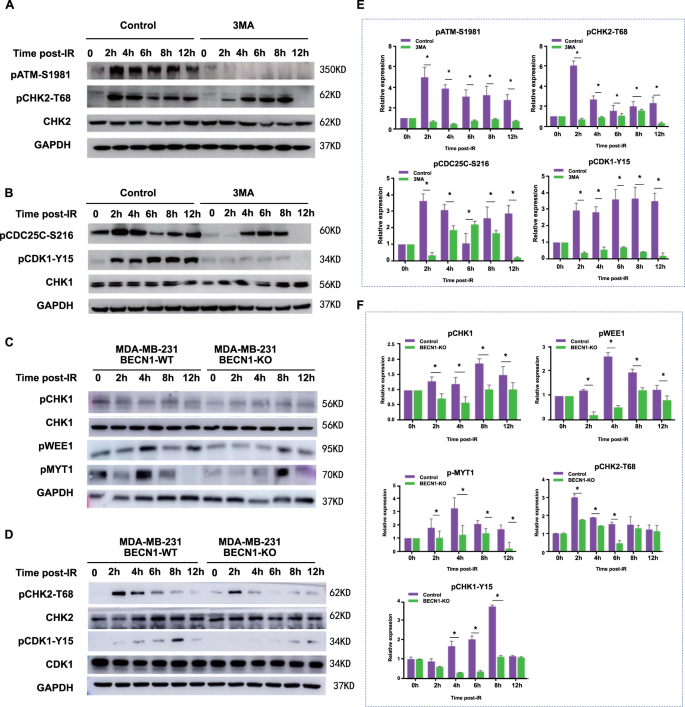
BECN1 promotes radiation-induced G2/M arrest through regulation CDK1 activity: a potential role for autophagy in G2/M checkpoint | Cell Death Discovery

Glaucocalyxin A induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway in human bladder cancer cells
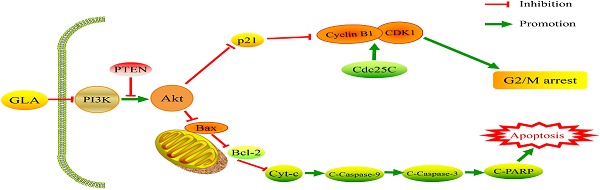
Glaucocalyxin A induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway in human bladder cancer cells

ATM–p53 pathway causes G2/M arrest, but represses apoptosis in pseudolaric acid B-treated HeLa cells - ScienceDirect
G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Tumor Selective Apoptosis of Acute Leukemia Cells by a Promising Benzophenone Thiosemicarbazone Compound | PLOS ONE

Proliferation Inhibition, DNA Damage, and Cell-Cycle Arrest of Human Astrocytoma Cells after Acrylamide Exposure | Chemical Research in Toxicology

ICD treatment causes cells cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. (A) The cell... | Download Scientific Diagram
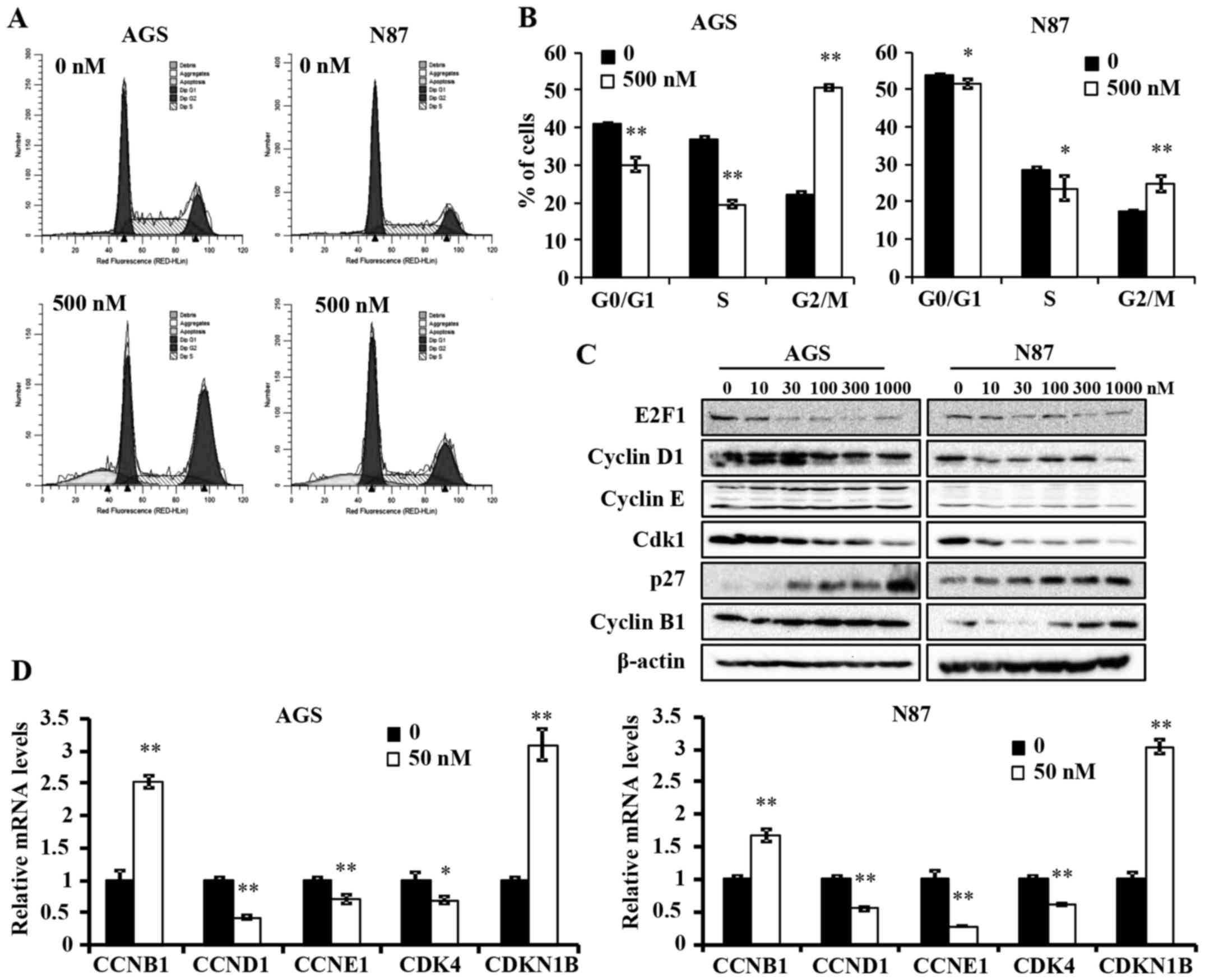
Ganetespib induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through targeting of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling
Cucurbitacin B Induced ATM-Mediated DNA Damage Causes G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest in a ROS-Dependent Manner | PLOS ONE

Effects of MT-6 on markers of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in ovarian... | Download Scientific Diagram

Cell cycle re-entry and arrest in G2/M phase induces senescence and fibrosis in Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy - ScienceDirect

Suppression of isoprenylcysteine carboxylmethyltransferase compromises DNA damage repair | Life Science Alliance
Isocorydine Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines by Inducing G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis | PLOS ONE

The overexpression of Plac9 induced G2/M phase arrest (A,B) The cell... | Download Scientific Diagram
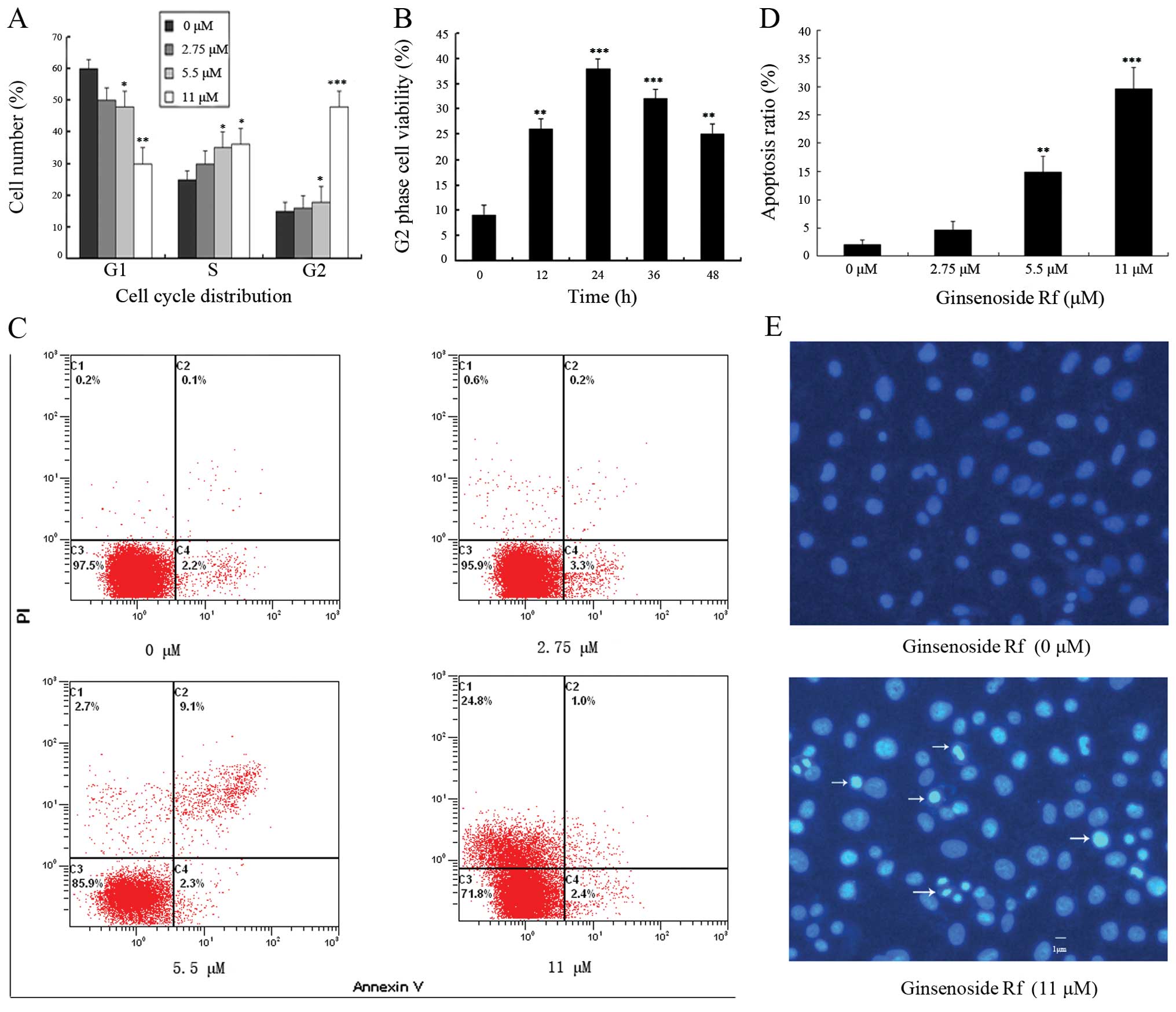
Induction of G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by ginsenoside Rf in human osteosarcoma MG‑63 cells through the mitochondrial pathway
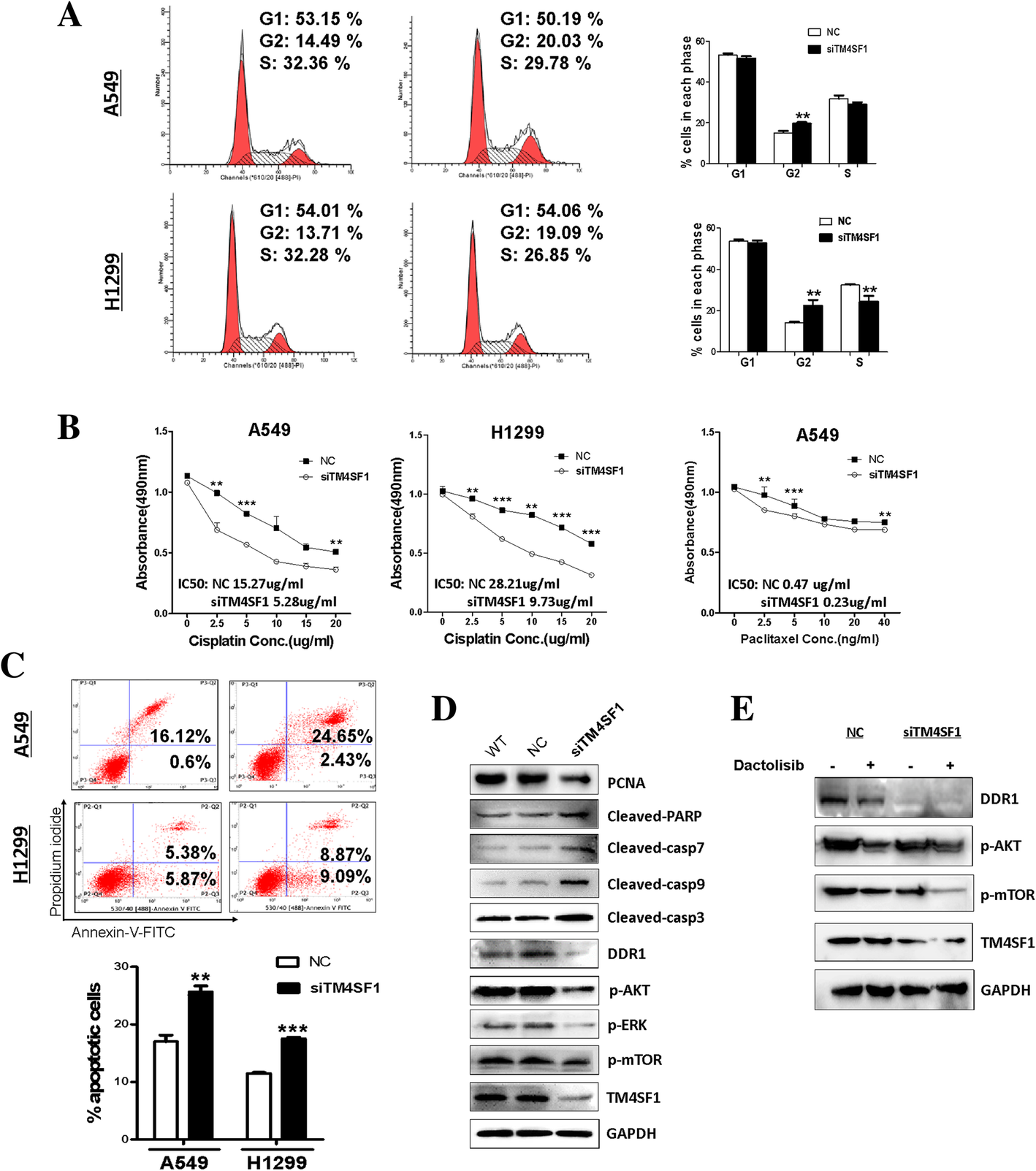
Transmembrane-4 L-six family member-1 (TM4SF1) promotes non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, invasion and chemo-resistance through regulating the DDR1/Akt/ERK-mTOR axis | Respiratory Research | Full Text
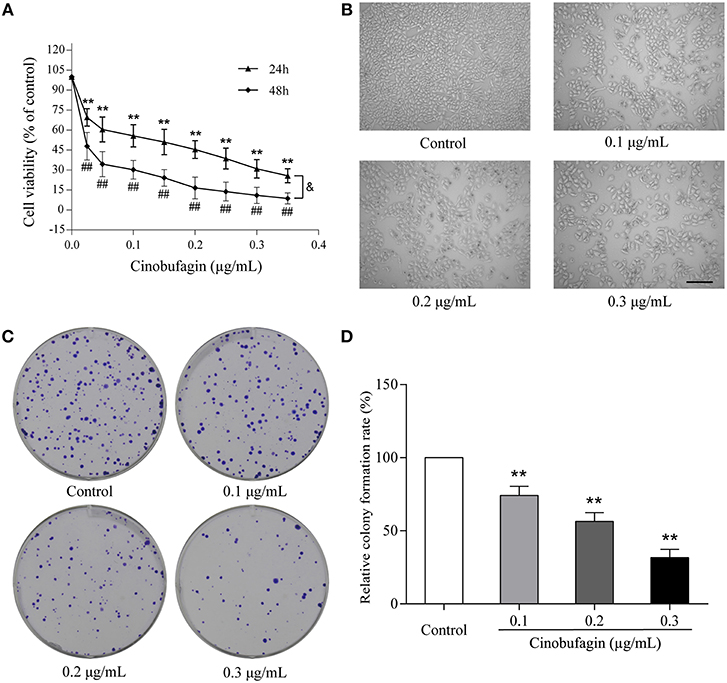
Frontiers | Cinobufagin Induces Cell Cycle Arrest at the G2/M Phase and Promotes Apoptosis in Malignant Melanoma Cells